Active Transport Involves All of the Following Except
Movement of water from soil to root. All of the following are examples of compounds that move by facilitated diffusion except.
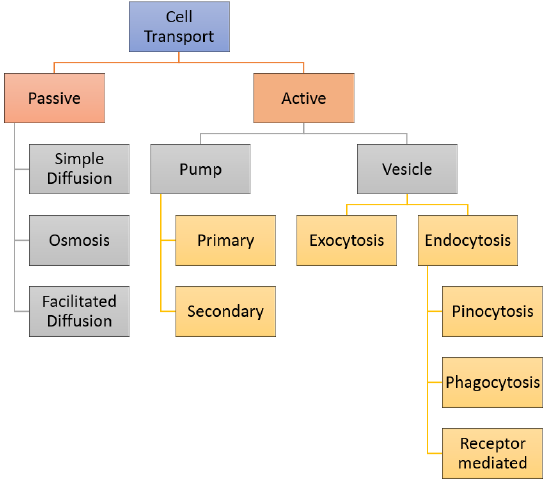
3 7 Cell Transport Biology Libretexts
23 All of the following involve active transport across membranes except A the movement of mineral nutrients from the apoplast to the symplast.

. Active transport is usually associated with accumulating high concentrations of molecules that the cell needs such as. 33 Reabsorption of filtered glucose from the lumen in. Products from RER are packaged into transport vesicles.
42 The following is a list of the steps involved in the process of secretion by the Golgi apparatus. Coupling to another transport system. B the movement of sugar from mesophyll cells into sieve-tube elements.
Transport of solute against a concentration gradient. Occurs predominantly via passive diffusion across the hair follicles sweat ducts and sebaceous glands. Occurs predominantly by active transport across the stratum corneum c.
D transport of solute against a concentration gradient. Facilitated diffusion allows certain kinds of compounds that are normally blocked by the cell membrane to cross the cell membrane. Transport in Plants Plant-Water Relations All the following involves osmosis exce.
All the following involves osmosis except. E a and c only. Tubular reabsorption involves all of the following except A active transport.
Active transport involves all of the following EXCEPT. A All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. C the movement of sugar from one sieve-tube element to the next.
C add thickness to woody organs. TL the plasma membrane. B In contrast to primary and secondary active transport neither facilitated dissusion nor simple diffusion requires additional energy and therefore can work in the absence of ATP.
Cy the direct use of ATP. E a and c only. Tubular reabsorption involves all of the following.
Active transport involves all of the following except the a diffusion of solute through the lipid bilayer of a membrane. B pumping of solutes across the membrane. The ability to concentrate the transported molecule.
Active cellular transportation ACT Unlike passive transport which uses the kinetic energy and natural entropy of molecules moving down a gradient active transport uses cellular energy to move them against a gradient polar repulsion or other resistance. C hydrolysis of ATP. Active transport systems are characterized by 1 movement of solutes against a concentration or electrochemical gradient 2 saturation at high solute concentration 3 specificity for structural andor chemical features of the solute 4 competitive inhibition by molecules transported by the same transporter and 5 inhibition of transport by compounds andor.
Occurs equally well across the skin from all parts of the body b. B pumping of solutes across the membrane. Vanishing cream is an ointment that may be classified as a A water soluble base b An oleaginous base c An absorption base d An emulsion base e.
B All cells arise from other pre-existing cells c All eukaryotic cells contain symbiotic. D transport of solute against a concentration gradient. Lymph transport involves all of the following EXCEPT _____.
C secondary active transport. Lymph transport involves all but which of the following. The nurse is caring for a patient who had minimally invasive surgery MIS for testicular cancer.
Bio 18 Unit 4 Practice Questions B facilitated diffusion. 213 Tubular reabsorption involves all of the following except A active transport. Secretory vesicles formed at the maturing face.
Vesicles arrive at forming face. Secondary active transport involves all of the. C a specific transport protein in the membrane.
The breakdown of ATP. B hydrolysis of ATP. Asked Nov 8 2021 in Anatomy Physiology by Boris.
2 Active transport involves all of the following except the. Involves passive diffusion across the dried keratin-filled cells of the stratum corneum d. A lymph capillary minivalve action B milking action of active muscle fibers C thorax pressure changes during breathing D smooth muscle contraction in the lymph capillary walls.
Material moves from cisterna to cisterna by means of transfer vesicles. Pumping of solutes across the membrane. E specific transport protein in the membrane.
Movement of water between xylem elements. 32 Tubular reabsorption involves all of the following except A active transport. A slow movement through the lipid bilayer of a membrane.
2Endocytosis and exocytosis are forms of active transport. 2 Active transport involves all of the following except A pumping of solutes across the membrane. E stem cell movements.
The nurse is also caring for a patient who had an open radical retroperitoneal lymph node dissection for testicular. This preview shows page 27 - 29 out of 44 pages. Movement of water from root hair to endodermis and pericycle.
E stem cell movements. Diffusion of solute through the lipid bilayer of a membrane. 11 A soil well suited for the growth of most plants would have all of the following properties EXCEPT.
Active transport differs from facilitated transport in following ways except a Carrier is involved b It is against concentration gradient c Energy is required d All of the above 36. 1Osmosis is a form of passive transport. Secondary active transport involves all of the following except x.
C hydrolysis of atp. D elongate shoots and roots. Diffusion displays saturation kinetics and involves a carrier protein.
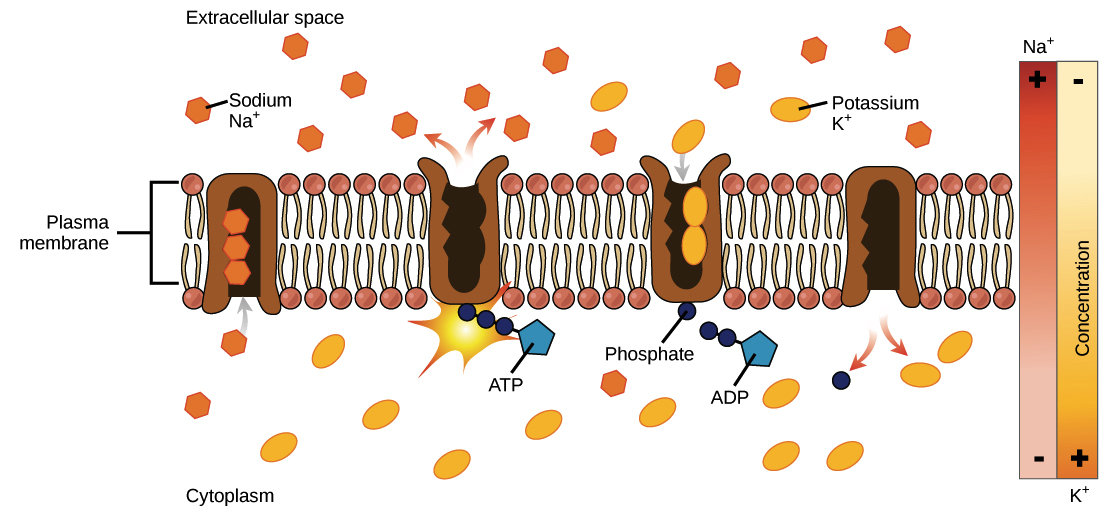
Active Transport Review Article Khan Academy

Phagocytosis Cell Transport Phagocytosis Involves The Extension From The Cell Sponsored Involves Extension C Cell Transport Cell Extracellular Fluid

No comments for "Active Transport Involves All of the Following Except"
Post a Comment